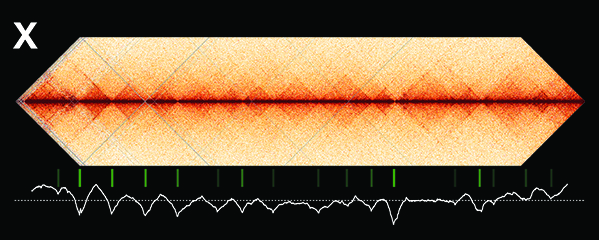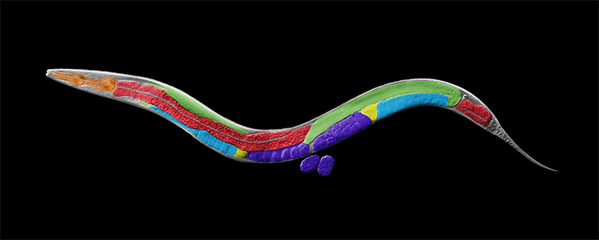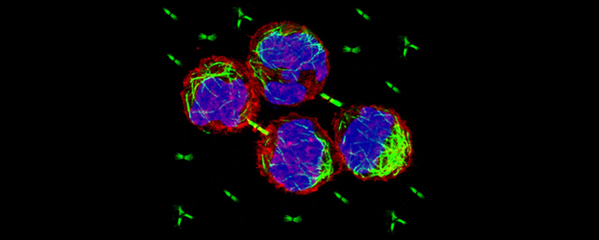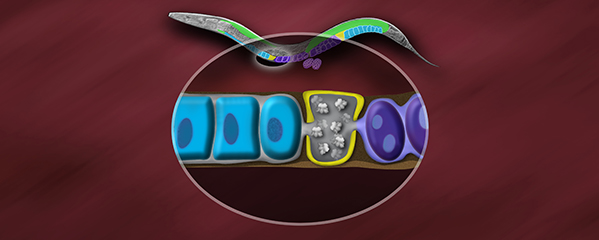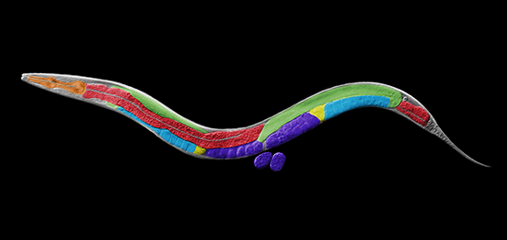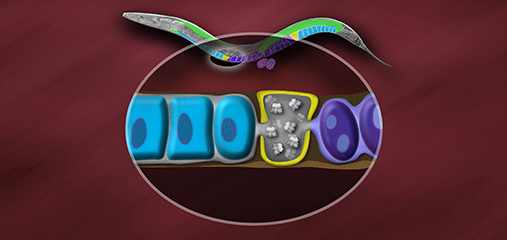


Crane, E., Bian, Q., McCord, R.P., Lajoie, B.R., Wheeler, B. S., Ralston, E.J., Uzawa, S., Dekker, J., Meyer, B.J. (2015) Condensin-driven remodelling of X chromosome topology during dosage compensation. Nature, 1 June 2015 doi:10.1038/nature14450 [PDF]
Maxwell, C., Kruesi, W.S.., Core, L., Kurhanewicz, N., Waters, C., Lewarch, C., Antoshechkin, A., Lis, J., Meyer, B.J., Baugh, L.R.. (2014) Pol II Docking and Pausing at Growth and Stress Genes in C. elegans. Cell Reports Volume 6, Issue 3, p455-466, 13 February 2014 [PDF]
Lo, T.W., Pickle, C.S., Lin, S., Ralston, E.J., Gurling, M., Schartner, C.M., Bian, Q., Doudna, J.A., Meyer, B.J. (2013) Precise and Heritable Genome Editing in Evolutionarily Diverse Nematodes Using TALENs and CRISPR/Cas9 to Engineer Insertions and Deletions. Genetics 195; 331-348. [PDF]
Farboud, B., Nix, P., Jow, M.M., Gladden, J.M., Meyer, B.J. (2013) Molecular antagonism between X-chromosome and autosome signals determines nematode sex. Genes & Development 27, 1159-1178. [PDF] [Supp.PDF]
Wood AJ*, Lo TW*, Zeitler B*, Pickle CS, Ralston EJ, Lee AH, Amora R, Miller JC, Leung E, Meng X, Zhang L, Rebar EJ, Gregory PD, Urnov FD, Meyer BJ. (2011) Targeted genome editing across species using ZFNs and TALENs. Science 333, 307. *These authors contributed equally to this work. [PDF] [Supp.PDF]
Youds, J. L., Mets, D. G., Mcllwraith, M. J., Martin, J. S., Ward, J. D., O'Neil, N. J., Rose, A. M., West, S. C., Meyer, B. J., Boulton, S. J. (2010) RTEL-1 Enforces Meiotic Crossover Interference and Homeostasis. Science 327, 1254-1258. [PDF]
Jans, J. Gladden, J. M., Ralston, E. J., Pickle, C. S., Michel, A. H., Pferdehirt, R. R., Eisen, M. B., Meyer, B. J. (2009) A condensin-like dosage compensation complex acts at a distance to control expression throughout the genome. Genes & Development 23 (5), 602-618. [PDF] [Supp.PDF]
Csankovszki, G., Collette, K., Spahl, K., Carey, J., Snyder, M., Petty, E., Patel, U., Tabuchi, T., Liu, H., McLeod, I., Thompson, J., Sarkesik, A., Yates, J., Meyer, B.J., Hagstrom, K. (2009) Three distinct condensin complexes control C. elegans chromosome dynamics. Current Biology 19 (1), 9-19. [PDF] [Supp.PDF]
Tsai, C.J., Mets, D.G., Albrecht, M.R., Nix, P., Chan, A., Meyer, B.J. (2008) Meiotic crossover number and distribution are regulated by a dosage compensation protein that resembles a condensin subunit. Genes & Development 22, 194-211. [PDF] [Supp.PDF]
Chu, D.S., Liu, H., Nix, P., Wu, T.F., Ralston, E.J., Yates, J.R., Meyer, B.J. (2006) Sperm chromatin proteomics identifies evolutionarily conserved fertility factors. Nature 443, 101-105. [PDF]
Meyer, B. J. X-Chromosome dosage compensation (June 25, 2005), WormBook, ed. The C. elegans Research Community, WormBook, doi/10.1895/wormbook.1.8.1, http://www.wormbook.org. [PDF]
Skop, A., Liu, H., Yates, J., Meyer, B., Heald, R. (2004) Dissection of the mammalian midbody proteome reveals conserved cytokinesis mechanisms. Science 305, 61-66. [PDF]
Chan, R., Chan, A., Jeon, M., Wu, T., Pasqualone, D., Rougvie, A., Meyer, B. (2003) Chromosome cohesion is regulated by C. elegans TIM-1, a paralog of the clock protein TIMELESS. Nature 423, 1002-1009. [PDF]
Luz, J.G., Hassig, C.A., Pickle, C., Godzik, A., Meyer, B.J., Wilson, I.A. (2003) XOL-1, Primary Determinant of Sexual Fate in C. elegans Is a GHMP Kinase Family Member and a Structural Prototype for a New Class of Developmental Regulators. Genes Dev. 17, 977-990. [PDF]
Chu, D.S., Dawes, H.E., Lieb, J.D., Chan, R.C., Kuo, A.F., and Meyer B.J. (2002) A Molecular Link between Gene-Specific and Chromosome-Wide Transcriptional Repression. Genes Dev. 16, 796-805. [PDF]
Hagstrom, K., Holmes, V., Cozzarelli, N., and Meyer, B.J. (2002) C. elegans Condensin Promotes Mitotic Chromosome Architecture, Centromere Organization, and Sister Chromatid Segregation during Mitosis and Meiosis. Genes Dev. 16, 729-742. [PDF]
Lieb, J.D., Oritz de Solorzano, C., Rodriguez, E.G., Jones, A., Angelo, M. Lockett, S. and Meyer, B.J. (2000) The C. elegans Dosage Compensation Machinery is Recruited to X-Chromosome DNA Attached to an Autosome. Genetics 156, 1603-1621. [PDF]


Yang, Q., Lo, T.-W., Brejc, K., Schartner, C., Ralston, E.J., Lapidus, D.M., and Meyer, B.J. (2023). X-Chromosome Target Specificity Diverged Between Dosage Compensation Mechanisms of Two Closely Related Caenorhabditis Species. eLife 12:e85413. DOI: 10.7554/eLife.85413. PMID: 36951246 PMCID: PMC10076027. [PDF]
Fuda, N.J., Brejc, K., Kruesi, W.S., Ralston, E.J., Bigley, R., Shin, A., Okada, M., and Meyer, B.J. (2022). Combinatorial Clustering of Distinct DNA Motifs Directs Synergistic Binding of Caenorhabditis elegans Dosage Compensation Complex to X Chromosomes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci., U.S.A. 119: e2211642119. DOI: 10.1073/pnas.2211642119. PMID: 36067293 PMCID: PMC947739. [PDF]
Anderson, E.A., Frankino, P.A., Higuchi-Sanabria, R., Yang, Q., Bian, Q., Podshivalova, K., Shin, A., Kenyon, C., Dillin, A., Meyer, B.J. (2019). X Chromosome Domain Architecture Regulates Caenorhabditis elegans Lifespan but Not Dosage Compensation. Developmental Cell (Epub 5 September 2019). [PDF]
Yin, D., Schwarz, E.M., Thomas, C.G., Felde, R.L., Korf, I.F., Cutter, A.D., Schartner, C.M., Ralston, E.J., Meyer, B.J., Haag, E.S. (2018). Rapid Genome Shrinkage in a Self-Fertile Nematode Reveals Sperm Competition Proteins. Science 359: 55-61. DOI: 10.1126/science.aao0827 PMID: 29302007 PMCID: PMC5789457 [PDF]
Brejc, K., Bian, Q., Uzawa, S., Wheeler, B.J., Anderson, E.C., King, D.S., Kranzusch, P.J., Preston, C.G., Meyer B.J. (2017) Dynamic Control of X Chromosome Conformation and Repression by a Histone H4K20 Demethylase. Cell, 2017 Sep 21;171(1):85-102.e23. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.07.041. Epub 2017 Aug 31. PubMed PMID: 28867287. [PDF]
Crane, E., Bian, Q., McCord, R.P., Lajoie, B.R., Wheeler, B. S., Ralston, E.J., Uzawa, S., Dekker, J., Meyer, B.J. (2015) Condensin-driven remodelling of X chromosome topology during dosage compensation. Nature, 1 June 2015 doi:10.1038/nature14450 [PDF]
Maxwell, C., Kruesi, W.S.., Core, L., Kurhanewicz, N., Waters, C., Lewarch, C., Antoshechkin, A., Lis, J., Meyer, B.J., Baugh, L.R.. (2014) Pol II Docking and Pausing at Growth and Stress Genes in C. elegans. Cell Reports Volume 6, Issue 3, p455-466, 13 February 2014 [PDF]
Lo, T.W., Pickle, C.S., Lin, S., Ralston, E.J., Gurling, M., Schartner, C.M., Bian, Q., Doudna, J.A., Meyer, B.J. (2013) Precise and Heritable Genome Editing in Evolutionarily Diverse Nematodes Using TALENs and CRISPR/Cas9 to Engineer Insertions and Deletions. Genetics 195; 331-348. [PDF]
Farboud, B., Nix, P., Jow, M.M., Gladden, J.M., Meyer, B.J. (2013) Molecular antagonism between X-chromosome and autosome signals determines nematode sex. Genes & Development 27, 1159-1178. [PDF] [Supp.PDF]
Wood AJ*, Lo TW*, Zeitler B*, Pickle CS, Ralston EJ, Lee AH, Amora R, Miller JC, Leung E, Meng X, Zhang L, Rebar EJ, Gregory PD, Urnov FD, Meyer BJ. (2011) Targeted genome editing across species using ZFNs and TALENs. Science 333, 307. *These authors contributed equally to this work. [PDF] [Supp.PDF]
Youds, J. L., Mets, D. G., Mcllwraith, M. J., Martin, J. S., Ward, J. D., O'Neil, N. J., Rose, A. M., West, S. C., Meyer, B. J., Boulton, S. J. (2010) RTEL-1 Enforces Meiotic Crossover Interference and Homeostasis. Science 327, 1254-1258. [PDF]
Jans, J. Gladden, J. M., Ralston, E. J., Pickle, C. S., Michel, A. H., Pferdehirt, R. R., Eisen, M. B., Meyer, B. J. (2009) A condensin-like dosage compensation complex acts at a distance to control expression throughout the genome. Genes & Development 23 (5), 602-618. [PDF] [Supp.PDF]
Csankovszki, G., Collette, K., Spahl, K., Carey, J., Snyder, M., Petty, E., Patel, U., Tabuchi, T., Liu, H., McLeod, I., Thompson, J., Sarkesik, A., Yates, J., Meyer, B.J., Hagstrom, K. (2009) Three distinct condensin complexes control C. elegans chromosome dynamics. Current Biology 19 (1), 9-19. [PDF] [Supp.PDF]
Tsai, C.J., Mets, D.G., Albrecht, M.R., Nix, P., Chan, A., Meyer, B.J. (2008) Meiotic crossover number and distribution are regulated by a dosage compensation protein that resembles a condensin subunit. Genes & Development 22, 194-211. [PDF] [Supp.PDF]
Chu, D.S., Liu, H., Nix, P., Wu, T.F., Ralston, E.J., Yates, J.R., Meyer, B.J. (2006) Sperm chromatin proteomics identifies evolutionarily conserved fertility factors. Nature 443, 101-105. [PDF]
Meyer, B. J. X-Chromosome dosage compensation (June 25, 2005), WormBook, ed. The C. elegans Research Community, WormBook, doi/10.1895/wormbook.1.8.1, http://www.wormbook.org. [PDF]
Skop, A., Liu, H., Yates, J., Meyer, B., Heald, R. (2004) Dissection of the mammalian midbody proteome reveals conserved cytokinesis mechanisms. Science 305, 61-66. [PDF]
Chan, R., Chan, A., Jeon, M., Wu, T., Pasqualone, D., Rougvie, A., Meyer, B. (2003) Chromosome cohesion is regulated by C. elegans TIM-1, a paralog of the clock protein TIMELESS. Nature 423, 1002-1009. [PDF]
Luz, J.G., Hassig, C.A., Pickle, C., Godzik, A., Meyer, B.J., Wilson, I.A. (2003) XOL-1, Primary Determinant of Sexual Fate in C. elegans Is a GHMP Kinase Family Member and a Structural Prototype for a New Class of Developmental Regulators. Genes Dev. 17, 977-990. [PDF]
Chu, D.S., Dawes, H.E., Lieb, J.D., Chan, R.C., Kuo, A.F., and Meyer B.J. (2002) A Molecular Link between Gene-Specific and Chromosome-Wide Transcriptional Repression. Genes Dev. 16, 796-805. [PDF]
Hagstrom, K., Holmes, V., Cozzarelli, N., and Meyer, B.J. (2002) C. elegans Condensin Promotes Mitotic Chromosome Architecture, Centromere Organization, and Sister Chromatid Segregation during Mitosis and Meiosis. Genes Dev. 16, 729-742. [PDF]
Lieb, J.D., Oritz de Solorzano, C., Rodriguez, E.G., Jones, A., Angelo, M. Lockett, S. and Meyer, B.J. (2000) The C. elegans Dosage Compensation Machinery is Recruited to X-Chromosome DNA Attached to an Autosome. Genetics 156, 1603-1621. [PDF]
Yang, Q., Lo, T.-W., Brejc, K., Schartner, C., Ralston, E.J., Lapidus, D.M., and Meyer, B.J. (2023). X-Chromosome Target Specificity Diverged Between Dosage Compensation Mechanisms of Two Closely Related Caenorhabditis Species. eLife 12:e85413. DOI: 10.7554/eLife.85413. PMID: 36951246 PMCID: PMC10076027 [PDF]
Fuda, N.J., Brejc, K., Kruesi, W.S., Ralston, E.J., Bigley, R., Shin, A., Okada, M., and Meyer, B.J. (2022). Combinatorial Clustering of Distinct DNA Motifs Directs Synergistic Binding of Caenorhabditis elegans Dosage Compensation Complex to X Chromosomes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci., U.S.A. 119: e2211642119. DOI: 10.1073/pnas.2211642119. PMID: 36067293 PMCID: PMC947739. [PDF]
Anderson, E.A., Frankino, P.A., Higuchi-Sanabria, R., Yang, Q., Bian, Q., Podshivalova, K., Shin, A., Kenyon, C., Dillin, A., Meyer, B.J. (2019). X Chromosome Domain Architecture Regulates Caenorhabditis elegans Lifespan but Not Dosage Compensation. Developmental Cell (Epub 5 September 2019). [PDF]
Yin, D., Schwarz, E.M., Thomas, C.G., Felde, R.L., Korf, I.F., Cutter, A.D., Schartner, C.M., Ralston, E.J., Meyer, B.J., Haag, E.S. (2018). Rapid Genome Shrinkage in a Self-Fertile Nematode Reveals Sperm Competition Proteins. Science 359: 55-61. DOI: 10.1126/science.aao0827 PMID: 29302007 PMCID: PMC5789457 [PDF]
Brejc, K., Bian, Q., Uzawa, S., Wheeler, B.J., Anderson, E.C., King, D.S., Kranzusch, P.J., Preston, C.G., Meyer B.J. (2017) Dynamic Control of X Chromosome Conformation and Repression by a Histone H4K20 Demethylase. Cell, 2017 Sep 21;171(1):85-102.e23. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.07.041. Epub 2017 Aug 31. PubMed PMID: 28867287. [PDF]
Crane, E., Bian, Q., McCord, R.P., Lajoie, B.R., Wheeler, B. S., Ralston, E.J., Uzawa, S., Dekker, J., Meyer, B.J. (2015) Condensin-driven remodelling of X chromosome topology during dosage compensation. Nature, 1 June 2015 doi:10.1038/nature14450 [PDF]
Maxwell, C., Kruesi, W.S.., Core, L., Kurhanewicz, N., Waters, C., Lewarch, C., Antoshechkin, A., Lis, J., Meyer, B.J., Baugh, L.R.. (2014) Pol II Docking and Pausing at Growth and Stress Genes in C. elegans. Cell Reports Volume 6, Issue 3, p455-466, 13 February 2014 [PDF]
Lo, T.W., Pickle, C.S., Lin, S., Ralston, E.J., Gurling, M., Schartner, C.M., Bian, Q., Doudna, J.A., Meyer, B.J. (2013) Precise and Heritable Genome Editing in Evolutionarily Diverse Nematodes Using TALENs and CRISPR/Cas9 to Engineer Insertions and Deletions. Genetics 195; 331-348. [PDF]
Farboud, B., Nix, P., Jow, M.M., Gladden, J.M., Meyer, B.J. (2013) Molecular antagonism between X-chromosome and autosome signals determines nematode sex. Genes & Development 27, 1159-1178. [PDF] [Supp.PDF]
Wood AJ*, Lo TW*, Zeitler B*, Pickle CS, Ralston EJ, Lee AH, Amora R, Miller JC, Leung E, Meng X, Zhang L, Rebar EJ, Gregory PD, Urnov FD, Meyer BJ. (2011) Targeted genome editing across species using ZFNs and TALENs. Science 333, 307. *These authors contributed equally to this work. [PDF] [Supp.PDF]
Youds, J. L., Mets, D. G., Mcllwraith, M. J., Martin, J. S., Ward, J. D., O'Neil, N. J., Rose, A. M., West, S. C., Meyer, B. J., Boulton, S. J. (2010) RTEL-1 Enforces Meiotic Crossover Interference and Homeostasis. Science 327, 1254-1258. [PDF]
Jans, J. Gladden, J. M., Ralston, E. J., Pickle, C. S., Michel, A. H., Pferdehirt, R. R., Eisen, M. B., Meyer, B. J. (2009) A condensin-like dosage compensation complex acts at a distance to control expression throughout the genome. Genes & Development 23 (5), 602-618. [PDF] [Supp.PDF]
Csankovszki, G., Collette, K., Spahl, K., Carey, J., Snyder, M., Petty, E., Patel, U., Tabuchi, T., Liu, H., McLeod, I., Thompson, J., Sarkesik, A., Yates, J., Meyer, B.J., Hagstrom, K. (2009) Three distinct condensin complexes control C. elegans chromosome dynamics. Current Biology 19 (1), 9-19. [PDF] [Supp.PDF]
Tsai, C.J., Mets, D.G., Albrecht, M.R., Nix, P., Chan, A., Meyer, B.J. (2008) Meiotic crossover number and distribution are regulated by a dosage compensation protein that resembles a condensin subunit. Genes & Development 22, 194-211. [PDF] [Supp.PDF]
Chu, D.S., Liu, H., Nix, P., Wu, T.F., Ralston, E.J., Yates, J.R., Meyer, B.J. (2006) Sperm chromatin proteomics identifies evolutionarily conserved fertility factors. Nature 443, 101-105. [PDF]
Meyer, B. J. X-Chromosome dosage compensation (June 25, 2005), WormBook, ed. The C. elegans Research Community, WormBook, doi/10.1895/wormbook.1.8.1, http://www.wormbook.org. [PDF]
Skop, A., Liu, H., Yates, J., Meyer, B., Heald, R. (2004) Dissection of the mammalian midbody proteome reveals conserved cytokinesis mechanisms. Science 305, 61-66. [PDF]
Chan, R., Chan, A., Jeon, M., Wu, T., Pasqualone, D., Rougvie, A., Meyer, B. (2003) Chromosome cohesion is regulated by C. elegans TIM-1, a paralog of the clock protein TIMELESS. Nature 423, 1002-1009. [PDF]
Luz, J.G., Hassig, C.A., Pickle, C., Godzik, A., Meyer, B.J., Wilson, I.A. (2003) XOL-1, Primary Determinant of Sexual Fate in C. elegans Is a GHMP Kinase Family Member and a Structural Prototype for a New Class of Developmental Regulators. Genes Dev. 17, 977-990. [PDF]
Chu, D.S., Dawes, H.E., Lieb, J.D., Chan, R.C., Kuo, A.F., and Meyer B.J. (2002) A Molecular Link between Gene-Specific and Chromosome-Wide Transcriptional Repression. Genes Dev. 16, 796-805. [PDF]
Hagstrom, K., Holmes, V., Cozzarelli, N., and Meyer, B.J. (2002) C. elegans Condensin Promotes Mitotic Chromosome Architecture, Centromere Organization, and Sister Chromatid Segregation during Mitosis and Meiosis. Genes Dev. 16, 729-742. [PDF]
Lieb, J.D., Oritz de Solorzano, C., Rodriguez, E.G., Jones, A., Angelo, M. Lockett, S. and Meyer, B.J. (2000) The C. elegans Dosage Compensation Machinery is Recruited to X-Chromosome DNA Attached to an Autosome. Genetics 156, 1603-1621. [PDF]
Yang, Q., Lo, T.-W., Brejc, K., Schartner, C., Ralston, E.J., Lapidus, D.M., and Meyer, B.J. (2023). X-Chromosome Target Specificity Diverged Between Dosage Compensation Mechanisms of Two Closely Related Caenorhabditis Species. eLife 12:e85413. DOI: 10.7554/eLife.85413. PMID: 36951246 PMCID: PMC10076027. [PDF]
Fuda, N.J., Brejc, K., Kruesi, W.S., Ralston, E.J., Bigley, R., Shin, A., Okada, M., and Meyer, B.J. (2022). Combinatorial Clustering of Distinct DNA Motifs Directs Synergistic Binding of Caenorhabditis elegans Dosage Compensation Complex to X Chromosomes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci., U.S.A. 119: e2211642119. DOI: 10.1073/pnas.2211642119. PMID: 36067293 PMCID: PMC947739. [PDF]
Anderson, E.A., Frankino, P.A., Higuchi-Sanabria, R., Yang, Q., Bian, Q., Podshivalova, K., Shin, A., Kenyon, C., Dillin, A., Meyer, B.J. (2019). X Chromosome Domain Architecture Regulates Caenorhabditis elegans Lifespan but Not Dosage Compensation. Developmental Cell (Epub 5 September 2019). [PDF]
Yin, D., Schwarz, E.M., Thomas, C.G., Felde, R.L., Korf, I.F., Cutter, A.D., Schartner, C.M., Ralston, E.J., Meyer, B.J., Haag, E.S. (2018). Rapid Genome Shrinkage in a Self-Fertile Nematode Reveals Sperm Competition Proteins. Science 359: 55-61. DOI: 10.1126/science.aao0827 PMID: 29302007 PMCID: PMC5789457 [PDF]
Brejc, K., Bian, Q., Uzawa, S., Wheeler, B.J., Anderson, E.C., King, D.S., Kranzusch, P.J., Preston, C.G., Meyer B.J. (2017) Dynamic Control of X Chromosome Conformation and Repression by a Histone H4K20 Demethylase. Cell, 2017 Sep 21;171(1):85-102.e23. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.07.041. Epub 2017 Aug 31. PubMed PMID: 28867287. [PDF]
Crane, E., Bian, Q., McCord, R.P., Lajoie, B.R., Wheeler, B. S., Ralston, E.J., Uzawa, S., Dekker, J., Meyer, B.J. (2015) Condensin-driven remodelling of X chromosome topology during dosage compensation. Nature, 1 June 2015 doi:10.1038/nature14450 [PDF]
Maxwell, C., Kruesi, W.S.., Core, L., Kurhanewicz, N., Waters, C., Lewarch, C., Antoshechkin, A., Lis, J., Meyer, B.J., Baugh, L.R.. (2014) Pol II Docking and Pausing at Growth and Stress Genes in C. elegans. Cell Reports Volume 6, Issue 3, p455-466, 13 February 2014 [PDF]
Lo, T.W., Pickle, C.S., Lin, S., Ralston, E.J., Gurling, M., Schartner, C.M., Bian, Q., Doudna, J.A., Meyer, B.J. (2013) Precise and Heritable Genome Editing in Evolutionarily Diverse Nematodes Using TALENs and CRISPR/Cas9 to Engineer Insertions and Deletions. Genetics 195; 331-348. [PDF]
Farboud, B., Nix, P., Jow, M.M., Gladden, J.M., Meyer, B.J. (2013) Molecular antagonism between X-chromosome and autosome signals determines nematode sex. Genes & Development 27, 1159-1178. [PDF] [Supp.PDF]
Wood AJ*, Lo TW*, Zeitler B*, Pickle CS, Ralston EJ, Lee AH, Amora R, Miller JC, Leung E, Meng X, Zhang L, Rebar EJ, Gregory PD, Urnov FD, Meyer BJ. (2011) Targeted genome editing across species using ZFNs and TALENs. Science 333, 307. *These authors contributed equally to this work. [PDF] [Supp.PDF]
Youds, J. L., Mets, D. G., Mcllwraith, M. J., Martin, J. S., Ward, J. D., O'Neil, N. J., Rose, A. M., West, S. C., Meyer, B. J., Boulton, S. J. (2010) RTEL-1 Enforces Meiotic Crossover Interference and Homeostasis. Science 327, 1254-1258. [PDF]
Jans, J. Gladden, J. M., Ralston, E. J., Pickle, C. S., Michel, A. H., Pferdehirt, R. R., Eisen, M. B., Meyer, B. J. (2009) A condensin-like dosage compensation complex acts at a distance to control expression throughout the genome. Genes & Development 23 (5), 602-618. [PDF] [Supp.PDF]
Csankovszki, G., Collette, K., Spahl, K., Carey, J., Snyder, M., Petty, E., Patel, U., Tabuchi, T., Liu, H., McLeod, I., Thompson, J., Sarkesik, A., Yates, J., Meyer, B.J., Hagstrom, K. (2009) Three distinct condensin complexes control C. elegans chromosome dynamics. Current Biology 19 (1), 9-19. [PDF] [Supp.PDF]
Tsai, C.J., Mets, D.G., Albrecht, M.R., Nix, P., Chan, A., Meyer, B.J. (2008) Meiotic crossover number and distribution are regulated by a dosage compensation protein that resembles a condensin subunit. Genes & Development 22, 194-211. [PDF] [Supp.PDF]
Chu, D.S., Liu, H., Nix, P., Wu, T.F., Ralston, E.J., Yates, J.R., Meyer, B.J. (2006) Sperm chromatin proteomics identifies evolutionarily conserved fertility factors. Nature 443, 101-105. [PDF]
Meyer, B. J. X-Chromosome dosage compensation (June 25, 2005), WormBook, ed. The C. elegans Research Community, WormBook, doi/10.1895/wormbook.1.8.1, http://www.wormbook.org. [PDF]
Skop, A., Liu, H., Yates, J., Meyer, B., Heald, R. (2004) Dissection of the mammalian midbody proteome reveals conserved cytokinesis mechanisms. Science 305, 61-66. [PDF]
Chan, R., Chan, A., Jeon, M., Wu, T., Pasqualone, D., Rougvie, A., Meyer, B. (2003) Chromosome cohesion is regulated by C. elegans TIM-1, a paralog of the clock protein TIMELESS. Nature 423, 1002-1009. [PDF]
Luz, J.G., Hassig, C.A., Pickle, C., Godzik, A., Meyer, B.J., Wilson, I.A. (2003) XOL-1, Primary Determinant of Sexual Fate in C. elegans Is a GHMP Kinase Family Member and a Structural Prototype for a New Class of Developmental Regulators. Genes Dev. 17, 977-990. [PDF]
Chu, D.S., Dawes, H.E., Lieb, J.D., Chan, R.C., Kuo, A.F., and Meyer B.J. (2002) A Molecular Link between Gene-Specific and Chromosome-Wide Transcriptional Repression. Genes Dev. 16, 796-805. [PDF]
Hagstrom, K., Holmes, V., Cozzarelli, N., and Meyer, B.J. (2002) C. elegans Condensin Promotes Mitotic Chromosome Architecture, Centromere Organization, and Sister Chromatid Segregation during Mitosis and Meiosis. Genes Dev. 16, 729-742. [PDF]
Lieb, J.D., Oritz de Solorzano, C., Rodriguez, E.G., Jones, A., Angelo, M. Lockett, S. and Meyer, B.J. (2000) The C. elegans Dosage Compensation Machinery is Recruited to X-Chromosome DNA Attached to an Autosome. Genetics 156, 1603-1621. [PDF]
Yang, Q., Lo, T.-W., Brejc, K., Schartner, C., Ralston, E.J., Lapidus, D.M., and Meyer, B.J. (2023). X-Chromosome Target Specificity Diverged Between Dosage Compensation Mechanisms of Two Closely Related Caenorhabditis Species. eLife 12:e85413. DOI: 10.7554/eLife.85413. PMID: 36951246 PMCID: PMC10076027. [PDF]
Fuda, N.J., Brejc, K., Kruesi, W.S., Ralston, E.J., Bigley, R., Shin, A., Okada, M., and Meyer, B.J. (2022). Combinatorial Clustering of Distinct DNA Motifs Directs Synergistic Binding of Caenorhabditis elegans Dosage Compensation Complex to X Chromosomes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci., U.S.A. 119: e2211642119. DOI: 10.1073/pnas.2211642119. PMID: 36067293 PMCID: PMC947739. [PDF]
Anderson, E.A., Frankino, P.A., Higuchi-Sanabria, R., Yang, Q., Bian, Q., Podshivalova, K., Shin, A., Kenyon, C., Dillin, A., Meyer, B.J. (2019). X Chromosome Domain Architecture Regulates Caenorhabditis elegans Lifespan but Not Dosage Compensation. Developmental Cell (Epub 5 September 2019). [PDF]
Yin, D., Schwarz, E.M., Thomas, C.G., Felde, R.L., Korf, I.F., Cutter, A.D., Schartner, C.M., Ralston, E.J., Meyer, B.J., Haag, E.S. (2018). Rapid Genome Shrinkage in a Self-Fertile Nematode Reveals Sperm Competition Proteins. Science 359: 55-61. DOI: 10.1126/science.aao0827 PMID: 29302007 PMCID: PMC5789457 [PDF]
Brejc, K., Bian, Q., Uzawa, S., Wheeler, B.J., Anderson, E.C., King, D.S., Kranzusch, P.J., Preston, C.G., Meyer B.J. (2017) Dynamic Control of X Chromosome Conformation and Repression by a Histone H4K20 Demethylase. Cell, 2017 Sep 21;171(1):85-102.e23. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.07.041. Epub 2017 Aug 31. PubMed PMID: 28867287. [PDF]
Crane, E., Bian, Q., McCord, R.P., Lajoie, B.R., Wheeler, B. S., Ralston, E.J., Uzawa, S., Dekker, J., Meyer, B.J. (2015) Condensin-driven remodelling of X chromosome topology during dosage compensation. Nature, 1 June 2015 doi:10.1038/nature14450 [PDF]
Maxwell, C., Kruesi, W.S.., Core, L., Kurhanewicz, N., Waters, C., Lewarch, C., Antoshechkin, A., Lis, J., Meyer, B.J., Baugh, L.R.. (2014) Pol II Docking and Pausing at Growth and Stress Genes in C. elegans. Cell Reports Volume 6, Issue 3, p455-466, 13 February 2014 [PDF]
Lo, T.W., Pickle, C.S., Lin, S., Ralston, E.J., Gurling, M., Schartner, C.M., Bian, Q., Doudna, J.A., Meyer, B.J. (2013) Precise and Heritable Genome Editing in Evolutionarily Diverse Nematodes Using TALENs and CRISPR/Cas9 to Engineer Insertions and Deletions. Genetics 195; 331-348. [PDF]
Farboud, B., Nix, P., Jow, M.M., Gladden, J.M., Meyer, B.J. (2013) Molecular antagonism between X-chromosome and autosome signals determines nematode sex. Genes & Development 27, 1159-1178. [PDF] [Supp.PDF]
Wood AJ*, Lo TW*, Zeitler B*, Pickle CS, Ralston EJ, Lee AH, Amora R, Miller JC, Leung E, Meng X, Zhang L, Rebar EJ, Gregory PD, Urnov FD, Meyer BJ. (2011) Targeted genome editing across species using ZFNs and TALENs. Science 333, 307. *These authors contributed equally to this work. [PDF] [Supp.PDF]
Youds, J. L., Mets, D. G., Mcllwraith, M. J., Martin, J. S., Ward, J. D., O'Neil, N. J., Rose, A. M., West, S. C., Meyer, B. J., Boulton, S. J. (2010) RTEL-1 Enforces Meiotic Crossover Interference and Homeostasis. Science 327, 1254-1258. [PDF]
Jans, J. Gladden, J. M., Ralston, E. J., Pickle, C. S., Michel, A. H., Pferdehirt, R. R., Eisen, M. B., Meyer, B. J. (2009) A condensin-like dosage compensation complex acts at a distance to control expression throughout the genome. Genes & Development 23 (5), 602-618. [PDF] [Supp.PDF]
Csankovszki, G., Collette, K., Spahl, K., Carey, J., Snyder, M., Petty, E., Patel, U., Tabuchi, T., Liu, H., McLeod, I., Thompson, J., Sarkesik, A., Yates, J., Meyer, B.J., Hagstrom, K. (2009) Three distinct condensin complexes control C. elegans chromosome dynamics. Current Biology 19 (1), 9-19. [PDF] [Supp.PDF]
Tsai, C.J., Mets, D.G., Albrecht, M.R., Nix, P., Chan, A., Meyer, B.J. (2008) Meiotic crossover number and distribution are regulated by a dosage compensation protein that resembles a condensin subunit. Genes & Development 22, 194-211. [PDF] [Supp.PDF]
Chu, D.S., Liu, H., Nix, P., Wu, T.F., Ralston, E.J., Yates, J.R., Meyer, B.J. (2006) Sperm chromatin proteomics identifies evolutionarily conserved fertility factors. Nature 443, 101-105. [PDF]
Meyer, B. J. X-Chromosome dosage compensation (June 25, 2005), WormBook, ed. The C. elegans Research Community, WormBook, doi/10.1895/wormbook.1.8.1, http://www.wormbook.org. [PDF]
Skop, A., Liu, H., Yates, J., Meyer, B., Heald, R. (2004) Dissection of the mammalian midbody proteome reveals conserved cytokinesis mechanisms. Science 305, 61-66. [PDF]
Chan, R., Chan, A., Jeon, M., Wu, T., Pasqualone, D., Rougvie, A., Meyer, B. (2003) Chromosome cohesion is regulated by C. elegans TIM-1, a paralog of the clock protein TIMELESS. Nature 423, 1002-1009. [PDF]
Luz, J.G., Hassig, C.A., Pickle, C., Godzik, A., Meyer, B.J., Wilson, I.A. (2003) XOL-1, Primary Determinant of Sexual Fate in C. elegans Is a GHMP Kinase Family Member and a Structural Prototype for a New Class of Developmental Regulators. Genes Dev. 17, 977-990. [PDF]
Chu, D.S., Dawes, H.E., Lieb, J.D., Chan, R.C., Kuo, A.F., and Meyer B.J. (2002) A Molecular Link between Gene-Specific and Chromosome-Wide Transcriptional Repression. Genes Dev. 16, 796-805. [PDF]
Hagstrom, K., Holmes, V., Cozzarelli, N., and Meyer, B.J. (2002) C. elegans Condensin Promotes Mitotic Chromosome Architecture, Centromere Organization, and Sister Chromatid Segregation during Mitosis and Meiosis. Genes Dev. 16, 729-742. [PDF]
Lieb, J.D., Oritz de Solorzano, C., Rodriguez, E.G., Jones, A., Angelo, M. Lockett, S. and Meyer, B.J. (2000) The C. elegans Dosage Compensation Machinery is Recruited to X-Chromosome DNA Attached to an Autosome. Genetics 156, 1603-1621. [PDF]