AMPA receptor/TARP stoichiometry visualized by single-molecule subunit counting
Abstract
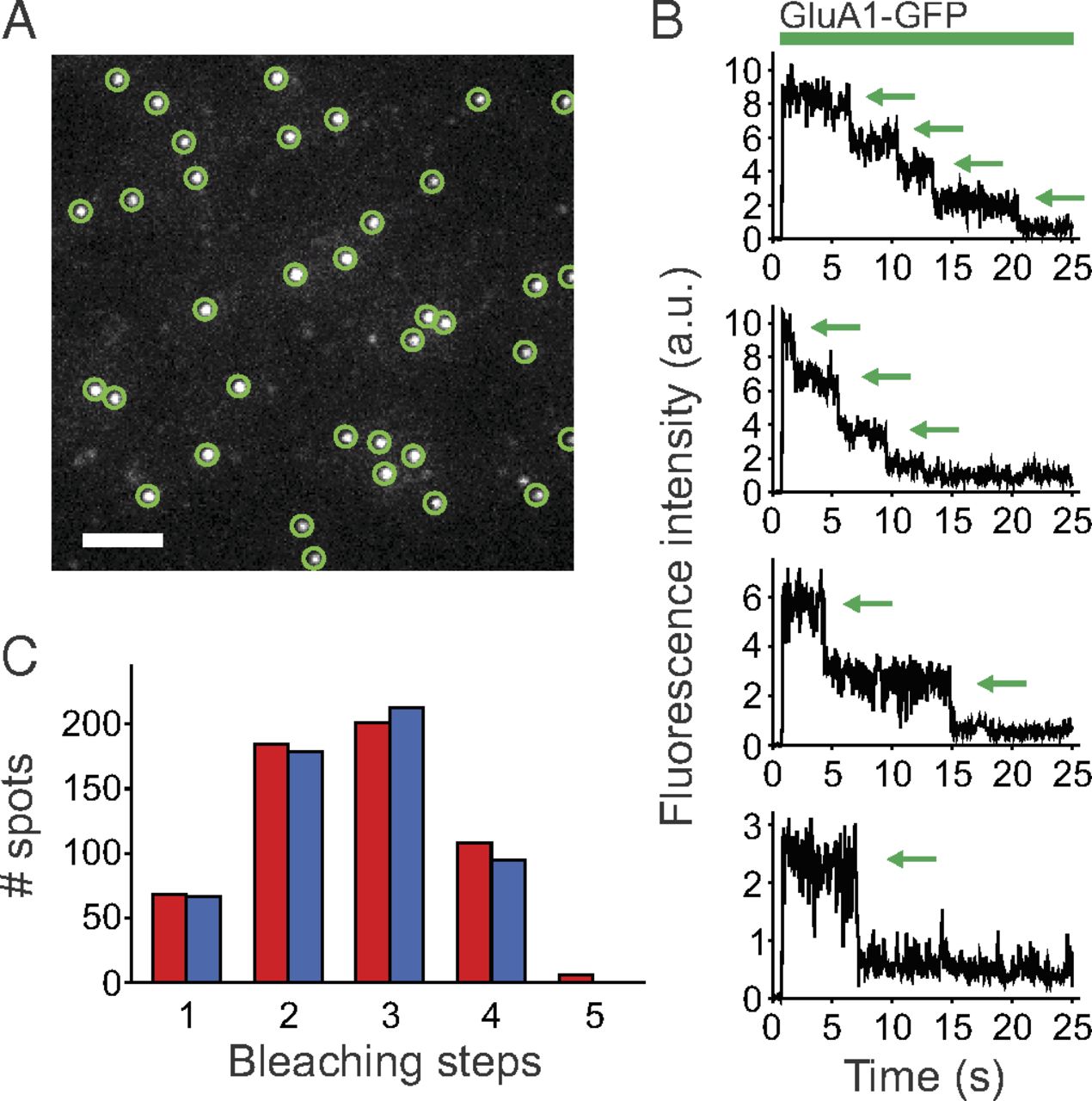
Members of the transmembrane AMPA receptor-regulatory protein (TARP) family modulate AMPA receptor (AMPA-R) trafficking and function. AMPA-Rs consist of four pore-forming subunits. Previous studies show that TARPs are an integral part of the AMPA-R complex, acting as accessory subunits for mature receptors in vivo. The TARP/AMPA-R stoichiometry was previously measured indirectly and found to be variable and dependent on TARP expression level, with at most four TARPs associated with each AMPA-R complex. Here, we use a single-molecule technique in live cells that selectively images proteins located in the plasma membrane to directly count the number of TARPs associated with each AMPA-R complex. Although individual GFP-tagged TARP subunits are observed as freely diffusing fluorescent spots on the surface of Xenopus laevis oocytes when expressed alone, coexpression with AMPA-R–mCherry immobilizes the stargazin-GFP spots at sites of AMPA-R–mCherry, consistent with complex formation. We determined the number of TARP molecules associated with each AMPA-R by counting bleaching steps for three different TARP family members: gamma-2, gamma-3, and gamma-4. We confirm that the TARP/AMPA-R stoichiometry depends on TARP expression level and discover that the maximum number of TARPs per AMPA-R complex falls into two categories: up to four gamma-2 or gamma-3 subunits, but rarely above two for gamma-4 subunit. This unexpected AMPA-R/TARP stoichiometry difference has important implications for the assembly and function of TARP/AMPA-R complexes.