MCB 32 Fall 2001
3rd Midterm Examination
60 Questions
December 14, 2001
Note: There were originally 60 questions on last years exam. I covered slightly different topics this year and so removed 6 questions that were on topics that were not covered this year.
- Which of the following is not a function of the lungs?
- delivers O2 from atmospheric air to the circulation.
- warm air to 37o
- saturates air with water
- All of the above are roles of the lungs.
- Gas exchange from the lumen of an alveolus to the blood:
- occurs across an alveolar cell and an endothelial cell
- occurs across only an alveolar cell
- occurs across only an endothelial cell
- involves both active and passive transport
- Normal expiration:
- requires contraction of the diaphragm
- is a passive process in which the lungs and chest wall relax back to their resting state.
- creates a pressure inside the lungs slightly less than atmospheric pressure
- All of the above
- A chamber contains the following:
3% CO2
25% O2
72 % N2
If the total chamber pressure is 800 mm Hg, what is the partial pressure of O2 in the chamber?
- 10 mm Hg
- 200 mm Hg
- 760 mm Hg
- 800 mm Hg
- Which of the following lies between the lungs and the chest wall and has a slight negative pressure at rest?
- alveolar space
- Bowman’s capsule
- interstitial space
- pleural space
- Surfactant:
- increases surface tension in the alveoli
- decreases surface tension in the alveoli
- increases surface tension in the capillaries
- decreases surface tension in the capillaries
- FEV1.0:
- is the volume of air than can be exhaled in 1 second after maximal inspiration.
- is the forced expiratory volume after 1 second.
- can be used to diagnose obstructive lung disorders.
- All of the above
- The tidal volume:
- is the volume left in the lungs after maximal expiration.
- is the volume left in the lungs after maximal inspiration
- is the volume left in the lungs after normal expiration.
- is the volume inhaled or exhaled during normal breathing.
- As air passes through the conducting zone:
- the partial pressure of O2 decreases
- the partial pressure of CO2 decreases
- the partial pressure of H20 decreases
- the partial pressure of N2 increases.
- At high altitudes:
- the amount of O2 dissolved in the blood will increase.
- plasma levels of 2,3 DPG should be less than at lower altitudes
- the affinity of hemoglobin for oxygen will increase
- None of the above
- Where is the partial pressure of CO2 the highest?
- in atmospheric air
- in the pulmonary vein
- in the pulmonary artery
- in the aorta
- In Figure 1 which point corresponds to the partial pressure of O2 in the arteries?
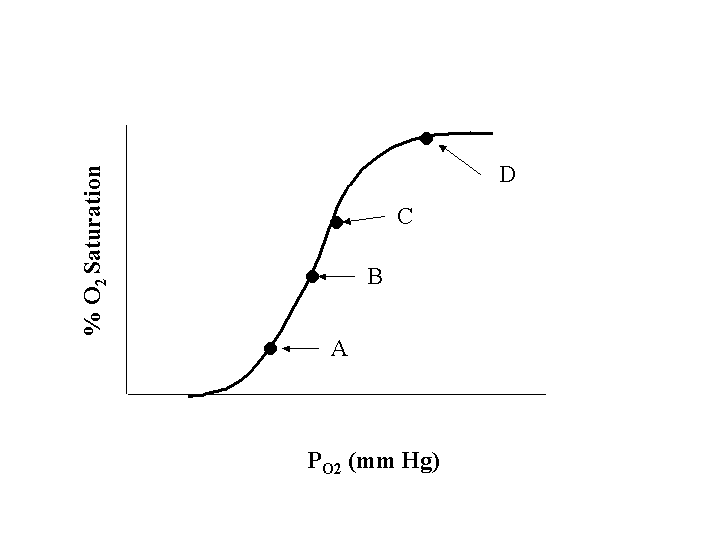
- A
- B
- C
- D
In Figure 2 which curve corresponds to the highest affinity of oxygen for hemoglobin?
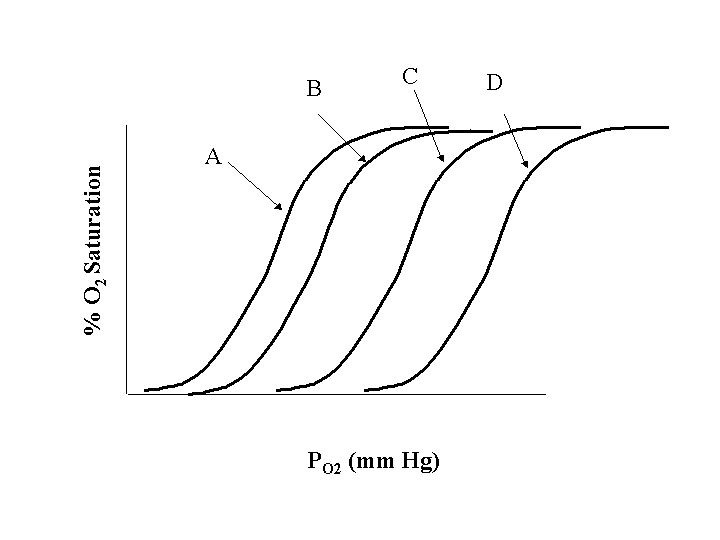
- A
- B
- C
- D
CO2 is transported from the tissues to the lung:
- dissolved in the blood
- bound to hemoglobin
- in the form of HCO3-
- All of the above
Chemoreceptors in the brain respond directly to
- plasma pH levels
- cerebral spinal fluid pH levels
- plasma CO2 levels
- cerebral spinal fluid CO2 levels
A drug binds to hemoglobin and prevents hemoglobin from binding H+. The drug thus decreases pH buffering by hemoglobin. Which of the following will occur?
- plasma pH will rise
- the O2 dissociation curve will shift to the left
- the O2 dissociation curve will shift to the right
- plasma HCO3- levels will rise.
The correct order of segments in the nephron is:
- Bowman’s capsule ®
loop of Henle ®
proximal tubule ®
distal tubule ®
collecting ducts
- Bowman’s capsule ®
proximal tubule ®
loop of Henle ®
collecting ducts ®
distal tubule
- Bowman’s capsule ®
proximal tubule ®
loop of Henle ®
distal tubule ®
collecting ducts
- Bowman’s capsule ®
proximal tubule ®
collecting ducts ®
loop of Henle ®
distal tubule
Peritubular capillaries are located:
- just before the afferent arteriole
- in between the efferent and afferent arterioles
- just after the afferent arteriole
- just after the efferent arteriole
In every nephron segment reabsorption of which of the following will always follow reabsorption of sodium?
- Cl-
- HCO3-
- H2O
- K+
In the nephron lumen, at the end of the proximal tubule:
- the sodium concentration is much higher than at the beginning of the proximal tubule
- the K+ concentration is much higher than at the beginning of the proximal tubule
- the glucose concentration is much lower than at the beginning of the proximal tubule
- the creatinine (muscle breakdown product) concentration is much lower than at the beginning of the proximal tubule
In the nephron lumen, at the end of the proximal tubule:
- the osmolarity is much higher than at the beginning of the proximal tubule
- the osmolarity is much lower than at the beginning of the proximal tubule
- the osmolarity is equal to the osmolarity at the beginning of the proximal tubule
- the osmolarity will depend on the amount of sodium reabsorption in the proximal tubule.
Glomerular filtration in a normal healthy adult is about:
- 5 liters/min
- 5 liters/day
- 180 liters/min
- 180 liters/day
Approximately 65% of the amount of fluid filtered at the glomerulus is reabsorbed in the:
- glomerulus
- proximal tubule
- collecting ducts
- juxtaglomerular apparatus
Glucose is transported in the proximal tubule:
- via the Na+K+-ATPase across the nephron lumen side
- down its concentration gradient from the nephron lumen to the inside of a kidney epithelial cell
- via the paracellular pathway
- via the transcellular pathway.
The main role of the loop of Henle is to:
- concentrate the filtrate in the nephron lumen in the cortical collecting ducts
- to concentrate solutes in the renal medullary interstitial space
- to concentrate solutes in the proximal tubule
- to concentrate solutes in the nephron lumen in the thick ascending
Which of the following would result in a very dilute urine?
- a drug that increases sodium reabsorption in the proximal tubule
- blocking receptors for antidiuretic hormone in the cortical collecting ducts.
- eating a meal high in sodium.
- increasing HCO3- reabsorption in the proximal tubule.
The osmolarity of sea water is:
- less than the osmolarity of plasma
- greater than the osmolarity in the nephron lumen at the end of the cortical collecting ducts when making a concentrated urine
- equal to the osmolarity in the renal medullary interstitial space.
- All of the above
In the proximal tubule, which of the following is involved in reabsorption of HCO3-?
- diffusion of CO2 across the nephron lumen side of the epithelial layer
- diffusion of HCO3- across the nephron lumen side of the epithelial layer.
- secretion of H+ into the nephron lumen
- A and C
In order to compensate for metabolic acidosis:
- the kidney secretes more H+
- the kidneys reabsorb more HCO3-
- the lungs expire more CO2
- All of the above
In order to convert CO2 into a hydrogen ion and a bicarbonate ion in the nephron lumen:
- the ammonia buffer must be present in the nephron lumen
- the phosphate buffer must be present in the nephron lumen
- carbonic anhydrase must be present in the nephron lumen
- All of the above
The liver drains into which of the following:
- pharynx
- duodenum
- large intestine
- rectum
The mucosal layer in the gastrointestinal system contains:
- parietal cells
- chief cells
- goblet cells
- All of the above
Which of the following could occur if the stomach were removed?
- an increase in the amount of amino acids in the gastrointestinal tract
- a decrease in the amount of monosaccharaides in the gastrointestinal tract
- increased chance of bacterial infections
- B and C
Stimulation of acid secretion involves:
- autonomic nerves
- hormones
- parietal cells
- All of the above
In the small intestine:
- microvilli increase the surface area for reabsorption
- many villi are found on cell membranes of the epithelial cells
- relative to the amount of fluid ingested, only a small amount is secreted.
- All of the above.
Brush border enzymes:
- digest disaccharides in the small intestine
- digest lipids in the small intestine
- allow water and carbon dioxide to combine to form a hydrogen ion and a bicarbonate ion.
- All of the above
Absorption of proteins and absorption of carbohydrates across the epithelial layer in the gastrointestinal tract involves:
- a Na+K+-ATPase
- a Na+ cotransporter
- passive diffusion across the blood side of the epithelial layer.
- All of the above
The primary function of the large intestine is:
- secretion of H+
- secretion of HCO3-
- absorption of water
- All of the above
Which of the following will result in diarrhea?
- an increase in osmolarity in the gastrointestinal tract
- an increase in sodium secretion into the gastrointestinal tract
- damage to the gastrointestinal wall
- All of the above
Which of the following substances use enterohepatic circulation:
- bile salts
- amino acids
- glucose
- All of the above
Acid secretion in the stomach is stimulated by:
- pepsinogen
- secretin
- gastrin
- cholecystokinin
Pancreatic secretion of trypsin is stimulated by:
- an increase in duodenal pH
- a decrease in duodenal pH
- fats in the small intestine
- fats in the large intestine.
The zygote:
- contains 23 chromosomes
- contains 23 pairs of homologous chromosomes
- is formed in the gonads around puberty
- is formed after multiple rounds of meiosis
The SRY gene (for testis determining factor):
- is found on the X chromosome
- encodes for a protein that will determine whether or not embryo contains an X or Y chromosome
- encodes for a protein than increases oogenesis
- encodes for a protein that determines whether or not the sex organs will be male or female.
Leydig cells:
- are found in the epididymis
- respond to both follicle stimulating hormone and leuteinizing hormone
- influence spermatogenesis
- add fructose and electrolytes to the semen.
Spermatogenesis:
- involves meiotic division
- involves mitotic division
- occurs within a Sertoli cell
- All of the above
Immediately after spermatogenesis, sperm are released into the:
- lumen of the seminiferous tubules
- Vas deferens
- seminal vesicles
- All of the above
The acrosome:
- is located near the head of the sperm
- contains proteolytic enzymes
- helps digest layers surrounding the oocyte
- All of the above
Semen:
- contains fructose
- is formed from secretions of the prostate gland
- contains substances that aid in fertilization of the oocyte.
- All of the above
The fallopian tube:
- transports fertilized oocytes from the ovary to the uterus
- transports sperm to the ovary for fertilization.
- surrounds the fetus during development
- All of the above
Oogenesis:
- occurs in the uterus
- occurs within a follicle
- results in the formation of many Graafian follicles
- All of the above
During the follicular phase of the menstrual cycle:
- progesterone levels reach their highest values
- progesterone stimulates the LH surge
- estrogen levels peak just prior to ovulation.
- All of the above
During the menstrual cycle a negative feedback loop occurs:
- just before ovulation
- during the follicular phase
- during the luteal phase
- None of the above
Fertilization occurs
- just before ovulation
- in the fallopian tubes
- in the uterus
- just prior to the LH surge
Answers
1.D 2.A 3.B 4.B 5.D 6.B 7.D 8.D 9.A 10.D 11.C 12.D 13.A 14.D 15.B 16.C 17.C 18.D 19.C 20.C 21.C 22.D 23.B 24.D 25.B 26.B 27.B 28.D 29.D 30.C 31.B 32.D 33.C 34.D 35.A 36.A 37.D 38.C 39.D 40.A 41.C 42.C 43.B 44.D 45.C 46.D 47.A 48.D 49.D 50.A 51.B 52.C 53.C 54.B

